Activation function defines the way the output is manipulated based on the input in a Neural Network. These functions must not only be differentiable but they are also mostly non-linear for determining a non-linear decision boundary using non-linear combinations of the input feature vector and weights. A few options for choosing activation function and their details are as under:
Identify function:
The identity function is the simplest possible activation function ; the resulting unit is called a linear associator which outputs continuous values
. The function is then used to implement a standard linear regression model for basic forecasting problems and therefore rarely used in neural networks.
Step function:
A step function originally used in a perceptron, outputs a certain value if the input value is above a certain threshold and it outputs another value if the input value is below the threshold. A example of this could be a binary step function which is used for binary classification, which outputs 1 if the input is above threshold and otherwise outputs 0. This function can also be used as feature identifiers in which these identifiers outputs a 1 if feature is present and 0 otherwise which can be incorporated in our models.
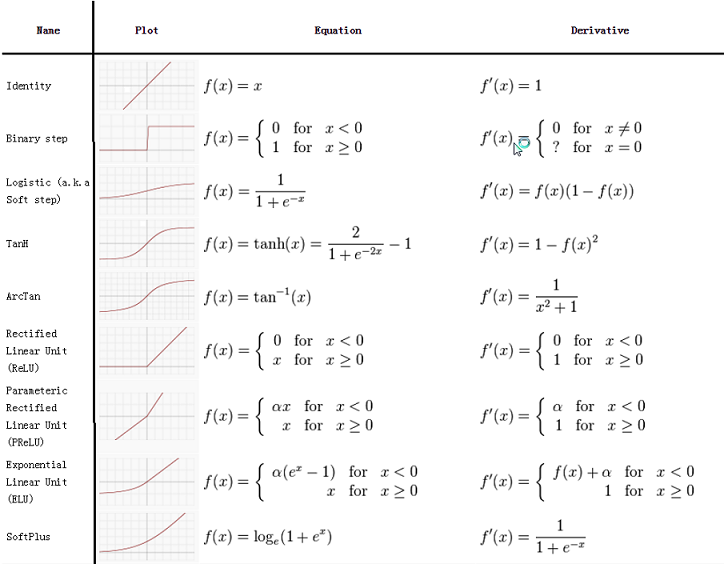
Logistic function:
Logistic function, kind of sigmoid function can be considered a modification of a step function, with an additional region of uncertainty. They are non-linear function with formula which maps the potential in the range (0, 1). In particular, large negative numbers become 0 and large positive numbers become 1. The functions are easy to implement as these functions are bounded unlike the identity functions and as they are easily differentiable.
TanH function:
Another form of sigmoid function is the hyperbolic tangent function which takes the mathematical form: which output value that range (-1, 1). As the range of output value is zero centered they have stronger gradients and thus are normally preferred over logistic functions. It is also seen that the hyperbolic-tangent and logistic activation functions are linearly related. Hence the predictions made by the hyperbolic-tangent and logistic functions are relatively same but their choice may depend on the training performance like in some studies it is observed that the time taken to train using hyperbolic tangent is less as compared with logistic function keeping the other parameters just the same.
Another kind of sigmoid function is the arctan function where which outputs value in range (
) . It can be used if input has high kurtosis but low skewness, to reduce the influence of extreme values.
Softmax function:
A Softmax function converts a raw value into a posterior probability and it is indeed a probability distribution over K different possible outcomes. The function is given by . These functions are used mostly in the final layer of multiclass classification models and in clustering models as it is easier to interpret standardized value (probability value) than a raw score.
Rectified linear unit (ReLU) function:
Rectified linear unit also called as the ramp function is computed as which means that the activation is simply thresholded at zero. Despite these activation function being not entirely differentiable (non-differentiable at 0), nor symmetric, and most of all, piece-wise linear they are widely used in a range of application from computer vision, speech recognition & deep neural networks. This is because of some useful properties of these functions that makes them computationally efficient and accelerates the convergence of stochastic gradient descent.
A smooth appromixation to the retifier is the analytic function also called as the softplus function is defined as . Both the ReLU and Softplus are largely similar, except near 0 where the softplus is enticingly smooth and differentiable.
There is one major disadvantage of using ReLU function is that if a large gradient is flowing through a ReLU, that could cause the weights to update in a way that the unit will never activate on any datapoint again and the unit is equivalent to have died. This can be managed in some way by adjusting the learning rate accordingly. However there is another alternative to solve this problem by slightly modifying the ReLU function to something known as the leaky ReLU function. Instead of making the function to equal to 0 when x>0, the leaky ReLU function will have a small negative slope. The mathematical eqvivalent is where
is a small constant. There are also other modification of ReLU function Parameteric rectified linear unit (PReLU), Randomized leaky rectified linear unit (RReLU), S-shaped rectified linear activation unit (SReLU). To read more on these please refer the link.
Maxout function:
The maxout activation function computes the maximum of a set of linear functions, and has the property that it can approximate any convex function of the input. The maxout function generalizes the ReLU and leaky ReLU by computing the function . The maxout function takes all the advantages of ReLU and also overcome their disadvantage with the implementation of Leaky ReLU but they in turn require but require many more parameters for learning compared to ReLU.
The best part about modeling is that we have all these functions readily available in libraries today and what we need to know is their application and functioning to apply them correctly for model optimization. As I use python, a few libraries which have inbuilt function to implement all these above activation functions are : Theano, TensorFlow, Keras, Lasagne, MXNet to name a few. Hope you found the article informative. Please do write in your views.
Further read: